EV Charging Methods Explained: How to Charge Smarter and Save More – Your Complete EV Charging Guide

Discover how EV charging works, explore 3 main charging types, compare costs of home vs. commercial chargers, and find expert-recommended charging and energy storage solutions.
1. How Does EV Charging Work? Principles & Charging Types Explained
New to electric vehicles and not sure which charging method suits your EV? Many first-time EV owners are unfamiliar with the differences between charger types—making it hard to choose the right one.
In this section, we’ll explain the core principles behind EV charging and introduce the 3 main types of EV chargers to help you get started.
(1) How EV Charging Works
Most residential and commercial power sources supply AC (alternating current), but electric vehicles require DC (direct current) to charge their batteries. That’s where EV chargers come in—they convert AC power into usable DC electricity for your vehicle.
Today’s EV chargers are classified into two main types based on how they convert power: AC chargers (slow charging) and DC chargers (fast charging).
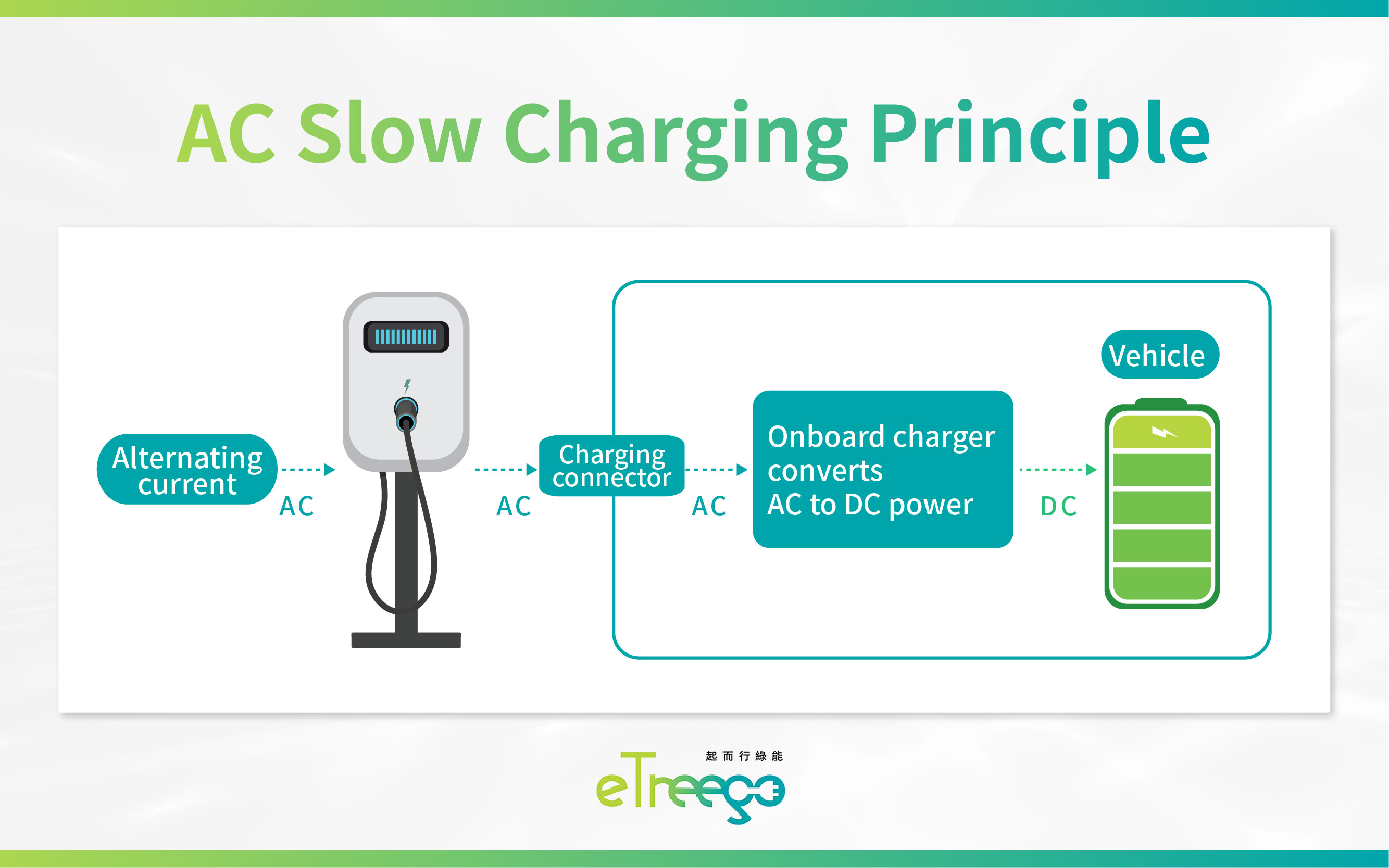
AC slow chargers work by delivering alternating current (AC) through the charging connector, which is then converted into direct current (DC) by the vehicle’s onboard charger. This DC power is used to charge the EV battery efficiently.
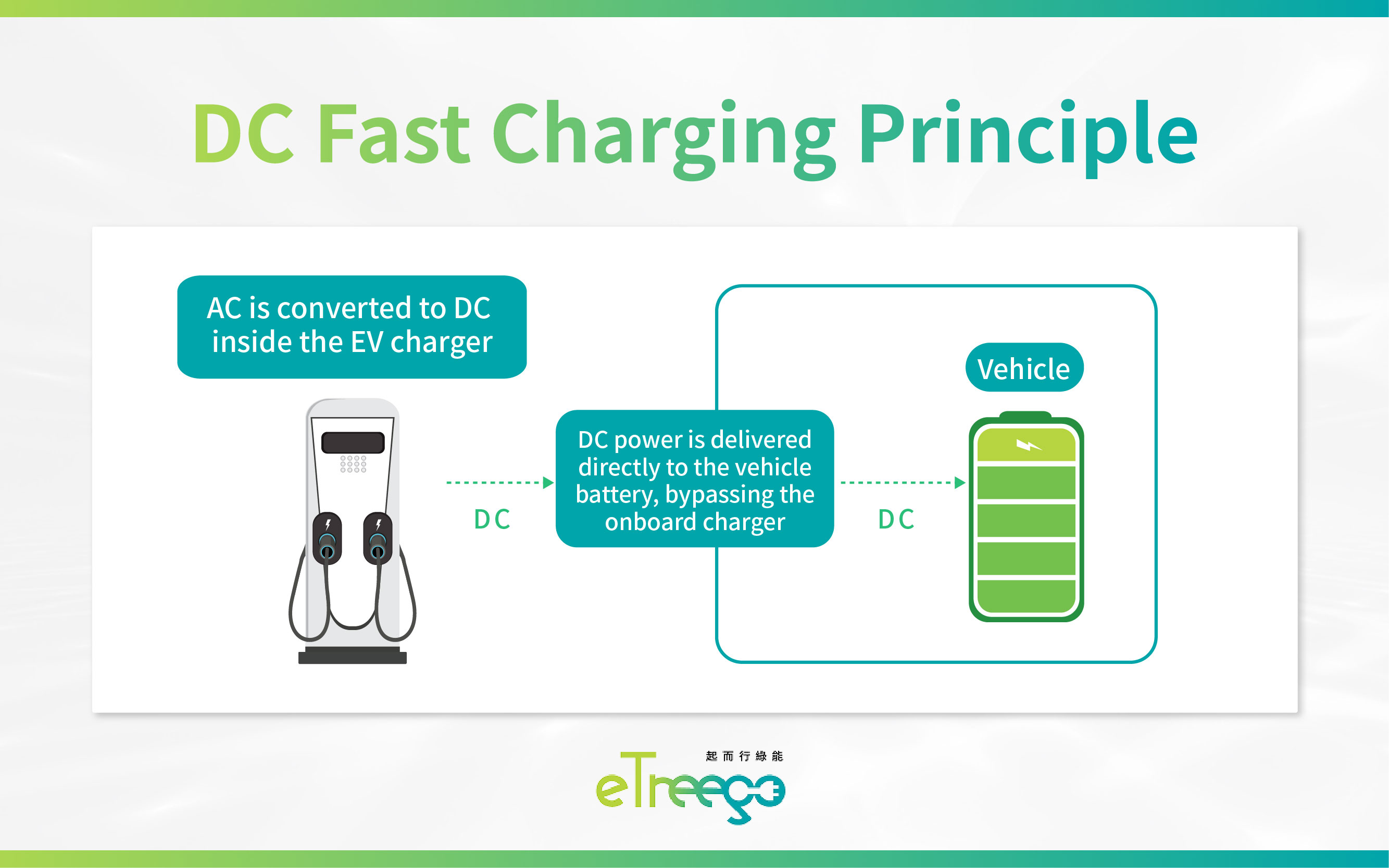
DC fast chargers convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) within the charger itself, then deliver the DC power directly to the EV’s battery for faster charging.
(2) The 3 Types of EV Chargers: Use-Based Classifications
Depending on different usage scenarios, EV chargers can be categorized into the following three types:
- Home EV Chargers: Designed for private residences or apartment communities, home chargers are primarily AC (slow chargers). They are more affordable to install and less likely to overload existing power systems. Some users who prefer faster charging opt for compact DC fast charging solutions at home.
- Public EV Chargers: Public chargers are installed in accessible locations and provide charging services to the public. These are mostly AC chargers, ideal for long-duration parking areas such as hotels, shopping malls, office buildings, and public parking lots.
- Commercial EV Chargers: Installed in business zones or commercial premises, these chargers typically use DC fast charging technology. They are commonly found at highway service areas, gas stations, and near freeway ramps—offering fast, convenient charging for EV drivers on the go.
How to Charge Your EV Efficiently? Learn More at eTreego!
2. How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV? Understanding AC vs. DC Charging Time and Range
(1) How to Estimate EV Charging Time – A Simple Formula
Wondering how long it takes to charge an electric vehicle at home or at a public/commercial charging station? It all depends on your target driving range (km) and the charging power output (kW). Here's a quick and easy formula to estimate charging time:
|
Assuming 1 kWh gives around 5 km of driving range: |
| Driving distance (km)/ 5 km = Energy needed (kWh) |
|
Estimate charging time: |
| Energy needed (kWh)/ Charger power (kW)= Charging time (hours) |
* Actual driving range per kWh may vary depending on vehicle model and efficiency.
Example: You need to drive 300 km.
Using the formula: 300 ÷ 5 = 60 kWh required
Compare charging time for a 7kW AC charger and a 350kW DC fast charger:
- 350kW fast charging: 60 ÷ 350 = 0.17 hours (~10 minutes)
- 7kW slow charging: 60 ÷ 7 = 8.57 hours
This shows that DC fast charging is ideal for quick turnarounds, while AC charging is better suited for overnight or long-duration parking.
(2) EV AC vs. DC Charging Efficiency Comparison Table
The table below offers a quick comparison between AC and DC EV chargers, helping drivers understand key differences in charging speed and functionality briefly. Let’s take a look.
| Category | AC Charger | DC Charger |
| Typical Applications | Residential, community, public parking | Commercial sites, small fast-charger |
| Charging Time | 6~12 hours for a full charge *varies by power output |
20~30 minutesto reach 80% charge * varies by power output |
| Estimated Range per Session | 7kW AC: ~35 km per hour | 350kW DC: ~30–100 km in 10 minutes |
| Common EV Charger Standards & Power Output | .Type 1(J1772): 3.7~19.2kW .Type 2(Mennekes): 3.7~22 kW .NACS(formerly TPC): 7.2~22 kW 。 |
.CCS1: Up to 350 kW (higher output requires liquid-cooled cables) .CCS2:Up to 350 kW (higher output requires liquid-cooled cables) .NACS(formerly TPC):Most common version offers 250 kW (Tesla V3); V4 supports up to 350 kW or more .CHAdeMO:Typically 50–100 kW; version 3.0 supports up to 500 kW, though real-world adoption remains limited |
3. How Much Does EV Charging Cost? Home vs. Commercial EV Charger Cost Comparison
Many EV owners and businesses often ask, “Is it expensive to install a charging station?” or “Which is more cost-effective—home or commercial charging?” Below is a detailed comparison of the cost structures for both.
(1) Home EV Charger Cost
If you're installing an AC charger at a private residence, the primary costs include:
- Installation Cost: Initial setup requires some investment, but it saves time and money in the long run by eliminating the need to visit commercial charging stations for emergencies.
- Electricity Cost: The charging electricity is simply added to your regular household utility bill.
For apartment or community housing, the cost structure is slightly different:
- Installation Shared by Residents: Installing shared chargers requires consent from the residential community or building management. Costs are typically divided among residents. In some cities, government subsidies are available to ease the financial burden.
- Electricity Paid by Users: Each user pays for the electricity they consume through smart metering or EMS (Energy Management System).
(2) Public and Commercial EV Charger Cost
Commercial EV chargers are built and operated by businesses. From the user's perspective, the only cost is the charging fee.
EV charging fees are not standardized. Pricing is typically determined by businesses based on factors such as location, charging speed, charger brand and quality, and the operator’s overall business strategy.
For businesses, although the initial investment in building a charging station can be significant, the long-term benefits are substantial. These include generating additional revenue, increasing customer dwell time, and enhancing brand visibility, all of which help attract more foot traffic.
As a result, more businesses are actively deploying EV chargers as a strategic business tool to boost operations and unlock new growth opportunities.
| EV Charger Type | Home EV Charger | Public / Commercial EV Charger |
| Installation Cost | • Detached house: Paid by the homeowner • Apartment/Community: Shared among residents |
Paid by the business owner |
| Electricity Cost | • Detached house: Included in the home electricity bill • Apartment/Community: Paid by the user |
Paid by the user, pricing set by the operator |
| Key Features | • Helps EV owners save on long-term charging costs • Convenient home charging—just plug in overnight • Community chargers may be eligible for government subsidies |
• EV drivers enjoy fast-charging convenience, but prices may vary • Offers strong business value—attracts customers and drives revenue |
Want to explore better EV charging solutions? Discover more with eTreego!
4. How to Find the Right EV Charging Station? Where to Charge for the Best Value? [EV Charging FAQ]
(1) How to Choose the Right EV Charger?
If you're looking for a charger that fits your EV and daily routine, consider the following 4 key principles:
- Charging Speed Requirements: For long parking durations, an AC charger is sufficient. If you need a quick top-up in a short time, opt for a DC fast charger.
- Check Your EV’s Charging Compatibility: In Taiwan, most EVs support CCS1 for DC fast charging and J1772 for AC slow charging. Always confirm your vehicle’s maximum charging capacity and plug type before selecting a charger.
- Use Charging Apps for Convenience: If you don’t have a home charger, EV charging apps can help locate nearby public or commercial charging stations with real-time availability and pricing.
- Choose a Reliable Charger Provider: For home installation, always go with an experienced and certified charging equipment provider to ensure safety, stability, and proper power distribution.
(2) Where Is the Most Cost-Effective Place to Charge Your EV?
Home chargers may involve a higher upfront installation cost, but they offer long-term savings by reducing reliance on paid commercial charging services.
If using public or commercial chargers, look for off-peak rates or promotional discounts. Some local governments also offer parking fee reductions or charging subsidies to encourage EV adoption, making public charging more affordable in select areas.
(3) How Many EV Chargers Are Available in Taiwan?
According to a 2024 report by CNA, Taiwan had a total of 10,086 public charging connectors by the end of November — including 7,681 AC slow chargers and 2,405 DC fast chargers.
Additionally, 15 highway service areas and the Caotun rest stop have been equipped with EV fast charging stations, offering 23 DC charging sites and 154 charging spots in total, ensuring nationwide access to high-efficiency EV charging.
5. Want Your Own EV Charger or Energy Storage System? Choose eTreego.
As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, so does the demand for reliable charging solutions. Wondering where to find high-quality, future-ready charging equipment? Let eTreego be your trusted partner.
Whether you're an EV owner looking to install a home EV charger, a business aiming to attract customers and generate new revenue, or an enterprise ready to build a custom energy storage system—eTreego offers the right solution for you.
Why choose eTreego? Here are our 3 key advantages:
- Expert Engineering Team: With years of experience in the EV industry, our technical team specializes in charging systems, motor control, vehicle integration, and battery management, ensuring every solution is engineered to perform.
- Comprehensive Charging Solutions: From 2-wheelers to 4-wheelers and even 8-wheel commercial vehicles, we provide a full range of EV chargers and smart energy management systems tailored to diverse field applications
- Trusted Industry Partnerships: Our strong collaborations with top-tier partners like Shihlin Electric, Hotai Motor, and major automakers guarantee superior service, product reliability, and future-ready technologies.
At eTreego, we’ve worked closely with leading technology and energy brands to develop proven, scalable EV charging and energy solutions. Visit our official website today to explore how our team can help you build the perfect EV infrastructure—efficient, safe, and built for tomorrow.
Explore Premium EV Charging Solutions – eTreego